The inverse head and shoulders pattern is one of the most well-known and widely studied formations in technical analysis. It is a visually distinctive pattern that often signals a shift from a bearish trend to a bullish one. Market participants use this pattern to identify potential buying opportunities, helping them enter long positions before a new upward trend gains momentum. By understanding its structure and the market psychology behind it, traders can better anticipate price movements and set more precise entry and exit points. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the defining features of the inverse head and shoulders pattern, discuss the behavioral factors that drive its formation, and outline effective trading strategies to maximize its potential.
Table of Contents
What is an Inverted Head and Shoulders Pattern?
Components of an Inverse Head and Shoulders Pattern
Psychology of the Inverse Head and Shoulders Pattern
Confirming the inverse head and shoulders pattern
How to Trade an Inverse Head and Shoulders Pattern
Tips for Trading Inverse Head and Shoulders Patterns
What is the best time frame to trade an inverse head and shoulders pattern?
Limitations and considerations
Key Takeaways
· Recognizable Reversal Pattern: The inverse head and shoulders is a reliable indicator of a potential bullish trend reversal following a sustained downtrend.
· Key Components and Confirmation: It consists of three troughs—a head and two shoulders—with a neckline resistance. A breakout above the neckline, ideally on high volume, confirms the pattern’s validity.
· Psychological Significance: The pattern reflects a shift in market sentiment as buyers gradually gain strength over sellers, creating higher lows and eventually breaching resistance.
· Flexible Across Markets and Timeframes: While commonly used in equities and forex, the inverse head and shoulders also appears in commodities and cryptocurrencies, and it’s applicable on multiple timeframes.
· Risk Management is Crucial: Although it’s a well-regarded pattern, using proper stop-loss levels and volume confirmation is essential to minimize risks and improve trading outcomes.
🔗 what
What is an Inverted Head and Shoulders Pattern?
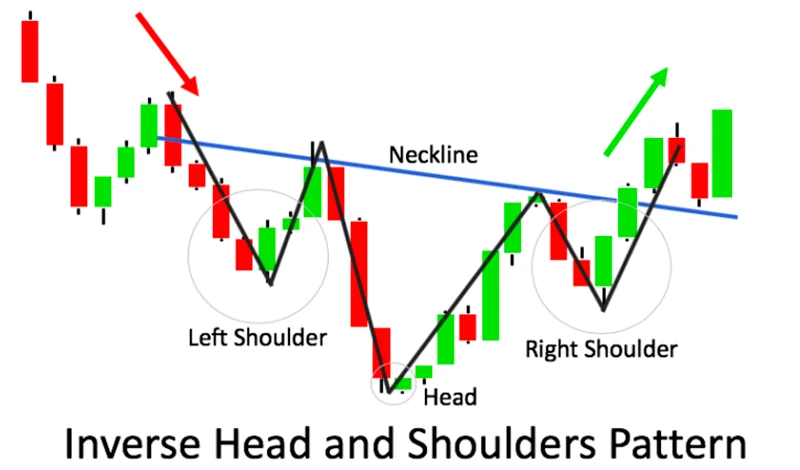
An inverted head and shoulders pattern, also known as a reverse head and shoulders, is a widely recognized chart formation that signals a potential bullish reversal in the market. This technical pattern typically emerges after a prolonged downtrend, serving as an indicator that selling momentum is waning and buyers are beginning to regain control. Its structure is distinct and relatively straightforward to identify, making it a popular tool among traders and analysts.
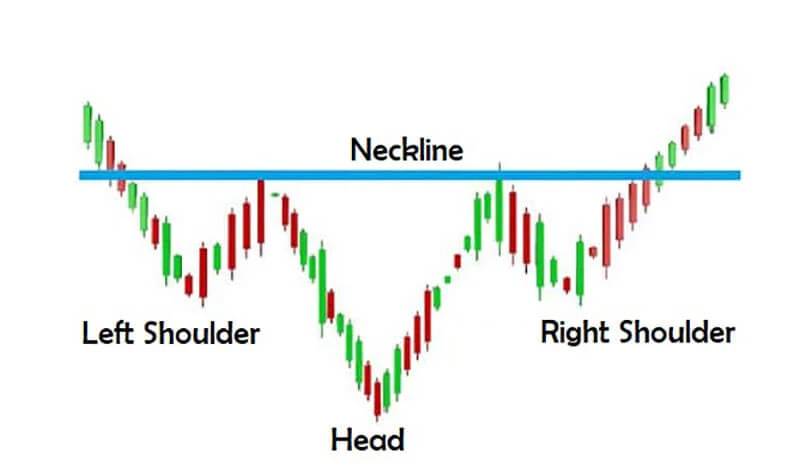
The pattern is characterized by three consecutive troughs. The first trough, known as the left shoulder, occurs as the market experiences a temporary dip before recovering slightly. Following this, the price dips even further, forming a deeper low called the head. This central trough is the lowest point of the pattern and marks a significant pivot in market sentiment. Finally, the price rises once more before declining again, but this time it forms a higher low, creating the right shoulder. This sequence of higher lows following the head indicates that downward pressure is diminishing.
A crucial component of the inverted head and shoulders pattern is the neckline. The neckline is a resistance level drawn by connecting the peaks that occur between the head and the two shoulders. The slope of the neckline can vary, sometimes slanting upward or appearing horizontal, but it remains an essential feature of the pattern. Once the price action decisively breaks above the neckline—preferably on increased volume—it confirms the pattern and suggests that the market is likely to reverse its trend, transitioning from bearish to bullish.
This breakout above the neckline is often interpreted as a strong buy signal. It indicates that the market has overcome a significant resistance level, and the momentum has shifted in favor of the bulls. Traders frequently use the pattern’s height—the vertical distance from the lowest point of the head to the neckline—to estimate the potential price target following the breakout. By adding this measured distance to the neckline breakout point, they can anticipate how far the price may rise during the ensuing uptrend.
🔗 components
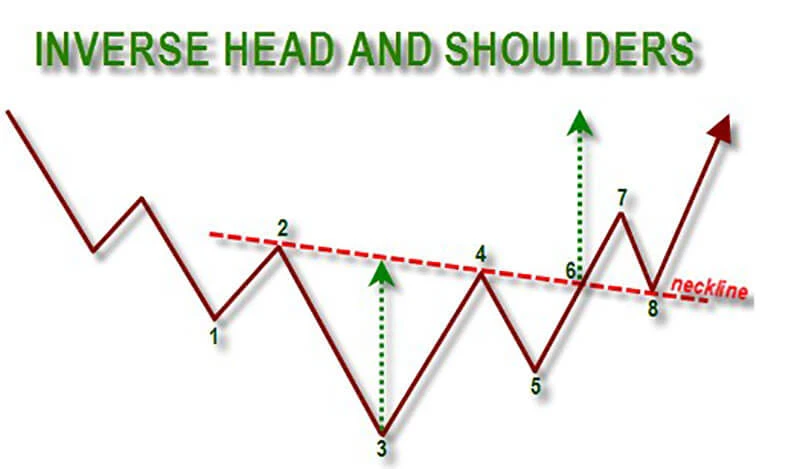
Components of an Inverse Head and Shoulders Pattern
1. The Left Shoulder:
The left shoulder forms as the price moves lower and then rebounds to create a short-term peak. This initial move is often a continuation of the existing downtrend.
2. The Head:
The head is the lowest point of the pattern, marking a significant trough. It reflects the market’s most bearish sentiment before a reversal begins to take shape.
3. The Right Shoulder:
After the head, the price rises once more and then dips again. However, this dip does not reach the depth of the head, creating the right shoulder.
4. The Neckline:
The neckline is drawn by connecting the highs that occur between the left shoulder, head, and right shoulder. This line often slopes slightly upwards but can also be horizontal. The neckline serves as the key resistance level that the price must break to confirm the pattern.
5. Volume Patterns:
Volume typically declines throughout the formation of the pattern. However, it often surges as the price breaks through the neckline, signaling strong buying interest.
🔗 psychology
Psychology of the Inverse Head and Shoulders Pattern
Understanding the psychology behind the inverse head and shoulders pattern is essential for traders looking to anticipate market shifts and act confidently. This pattern, at its core, reflects a profound change in sentiment—moving from despair and capitulation to renewed optimism and growing momentum.
Capitulation and Recovery:
At the heart of the inverse head and shoulders is the head itself—the lowest point of the pattern. This marks a moment of capitulation, where the prevailing downtrend is at its most extreme. Sellers, overwhelmed by pessimism, drive prices sharply lower. The market feels heavily one-sided, with few participants willing to step in and buy. However, this period of extreme bearishness can only last so long. As prices stabilize at this low level, a growing number of buyers see an opportunity. They begin to accumulate positions, believing the market is undervalued. This gradual increase in buying pressure signals the start of a recovery phase, pulling the price back up toward the neckline.
Shifting Sentiment:
The formation of the right shoulder provides critical psychological clues. After the dramatic drop that forms the head, the price rebounds but eventually pulls back again. However, this time the pullback does not reach the previous lows, suggesting that sellers are no longer as dominant. Traders and investors notice this higher low, interpreting it as a sign that the downward momentum is fading. Optimism starts to grow, and the crowd’s behavior shifts. Instead of panicking, more participants see potential upside. As the right shoulder forms, the balance between buyers and sellers begins to tip, increasing buying interest and setting the stage for a breakout.
Confirmation and Momentum:
The breakout above the neckline is the ultimate psychological turning point. For weeks or even months, the neckline has acted as a barrier—reflecting doubt, hesitation, and resistance. When the price finally surges through this level, it confirms what many traders have been suspecting: the bears are losing their grip. A wave of new buyers floods in, often resulting in a noticeable surge in volume. This breakout represents more than just a technical event; it’s a clear signal that market sentiment has decisively shifted. The surge in momentum, fueled by fresh enthusiasm, often propels prices higher, marking the beginning of a new uptrend.
🔗 confirming
Confirming the Inverse Head and Shoulders Pattern
Confirming an inverse head and shoulders pattern involves more than just spotting the familiar shape on a chart. While its visual structure is a key clue, the underlying market dynamics—such as price action, volume behavior, and follow-through—play a critical role in establishing the pattern’s credibility.
Breakout Above the Neckline:
The neckline, often seen as a major resistance level, acts as a proving ground for the pattern. A price close above this level signals that buyers have successfully overcome the resistance. However, for this confirmation to carry weight, the breakout must be both decisive and supported by strong volume. High volume on the breakout not only indicates that the pattern is genuine, but also suggests that the market is likely to sustain its newfound upward momentum.
Retest of the Neckline:
After breaking above the neckline, it’s not uncommon for the price to pull back slightly to retest this level. This retest serves as a second chance to confirm that the resistance level has turned into support. If the neckline holds firm during the retest and the price rebounds from it, the pattern’s reliability increases. This scenario provides additional confidence to traders, as it demonstrates that the market is respecting the new support level.
Volume Surge and Sustained Interest:
A key element in confirming any pattern, especially an inverse head and shoulders, is the behavior of volume. While a sharp volume increase on the breakout is a strong initial sign, the volume dynamics after the breakout also matter. Sustained volume or gradually increasing participation after the breakout suggests that the trend is not a fluke. This continued interest from buyers reinforces the idea that the market sentiment has truly shifted, and that the new uptrend is likely to hold.
By focusing on these confirmation steps—evaluating the breakout above the neckline, observing the reaction to a potential retest, and monitoring volume dynamics—traders can increase their confidence in the pattern’s validity. This, in turn, helps them make more informed decisions when entering positions, setting stop-loss levels, and managing their trades.
🔗 trade
How to Trade an Inverse Head and Shoulders Pattern
Trading an inverse head and shoulders pattern involves several key steps:
- Identify the Pattern Early: Watch for the formation of the left shoulder and the head. As the right shoulder starts to develop, anticipate the breakout point.
- Wait for Confirmation: Do not enter the trade until the price decisively breaks above the neckline on strong volume. Confirmation reduces the risk of false breakouts.
- Measure the Price Target: To estimate the target price, measure the vertical distance from the neckline to the lowest point of the head. Add this distance to the breakout point to determine the potential upside.
- Set a Stop-Loss Level: Place a stop-loss order below the right shoulder or the head’s low point. This provides a safety net if the pattern fails.
- Manage the Trade: As the price moves in your favor, consider adjusting your stop-loss to lock in profits. If the price approaches the target level, decide whether to close the position or let it run with a trailing stop.
🔗 tips
Tips for Trading Inverse Head and Shoulders Patterns
When trading an inverse head and shoulders pattern, a few best practices can improve your chances of success:
Ensure Proper Identification:
Confirm that the pattern includes distinct left and right shoulders, a clear head, and a well-defined neckline. If the formation is unclear or the shoulders are uneven, consider waiting for a more textbook setup.
Volume Confirmation:
A rise in volume on the breakout above the neckline can signal stronger momentum. If the breakout occurs on low volume, the reversal may lack conviction and be prone to failure.
Wait for a Retest:
Sometimes, the price will retest the neckline after breaking through it. This can provide an opportunity to enter the trade at a more favorable price, while also confirming that the pattern is holding.
Use Appropriate Stop-Losses:
Setting a stop-loss below the head or right shoulder can help protect your capital in case the pattern fails. Always have a well-defined risk management strategy.
Don’t Chase the Breakout:
If you missed the initial breakout, it’s often better to wait for a pullback than to enter at an extended level. Chasing the move can increase your risk and reduce potential reward.
Combine with Other Indicators:
Consider using additional technical indicators, such as moving averages or the relative strength index (RSI), to confirm the trend change and strengthen your trading decision.
🔗 best
What is the Best Time Frame to Trade an Inverse Head and Shoulders Pattern?
Determining the ideal time frame for trading an inverse head and shoulders pattern is not a one-size-fits-all decision. Instead, it hinges on your individual trading approach, the asset you’re analyzing, and the market conditions. Each time frame offers unique benefits and challenges, and your choice should align with your objectives and risk tolerance.
Short-Term Trading (Intraday Charts):
For traders who seek quick profits and are comfortable with fast-paced decision-making, shorter time frames such as 5-minute or 15-minute charts can be appealing. These intervals provide frequent opportunities to spot inverse head and shoulders formations, but they also come with increased market “noise” and higher susceptibility to false signals. Success in these time frames often depends on maintaining strict discipline, using precise entry and exit points, and paying close attention to intraday volatility.
Medium-Term Trading (4-Hour, Daily Charts):
Swing traders, who aim to capitalize on moves that unfold over several days or weeks, often prefer the balance provided by medium-term time frames. Patterns on these charts are generally more reliable than those on lower time frames, as they are less influenced by random price fluctuations. A 4-hour chart, for example, allows you to catch trend reversals without having to react instantly, while daily charts often present clearer and more definitive formations. However, patience is key, as waiting for the pattern to fully develop and confirm can take time.
Long-Term Trading (Weekly Charts):
Investors and long-term traders looking for substantial trend shifts may focus on weekly charts. In these longer time frames, an inverse head and shoulders pattern can signal a significant change in market direction, often accompanied by fundamental shifts in sentiment or economic conditions. While this approach requires considerable patience and larger stop-loss allowances, the reward can be capturing extensive moves that last for months or even years. These patterns tend to be highly reliable, as they reflect broader market consensus rather than short-term sentiment swings.
Additional Considerations:
- Pattern Clarity: No matter the time frame, the quality of the inverse head and shoulders pattern is paramount. A poorly defined pattern, with uneven shoulders or a weak neckline, is less likely to produce the expected results.
- Trend Strength and Market Context: Ensure that the broader trend and the market conditions support the pattern’s interpretation. For example, a strong overall downtrend may reduce the likelihood of success for an inverse head and shoulders on shorter time frames.
- Risk Management: Time frame also affects risk. Short-term charts demand tighter stop-losses, while longer-term charts may require broader risk parameters.
- Testing in a Demo Environment: Before trading a specific time frame live, it’s wise to backtest the pattern’s performance and practice on a demo account. This helps you understand the pattern’s reliability and gives you confidence in your chosen approach.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the time frame that best matches your trading style, ensuring a more methodical and informed approach to trading inverse head and shoulders patterns.
🔗 advantages
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Clear Entry and Exit Points: The neckline provides a well-defined level for entry. The measured move from the head to the neckline also offers a straightforward way to set price targets.
- Widespread Recognition: As one of the most well-known reversal patterns, many traders watch for it. This can lead to self-fulfilling breakouts as traders collectively buy upon confirmation.
- Flexibility Across Markets: The inverse head and shoulders pattern can be applied to stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies, making it a versatile tool in technical analysis.
Disadvantages:
- False Breakouts: Like all chart patterns, inverse head and shoulders setups are not foolproof. Breakouts can fail, resulting in losses if proper risk management is not in place.
- Subjectivity in Identification: Patterns are rarely perfect. Determining the exact neckline or confirming the head and shoulders can sometimes be subjective, leading to errors in analysis.
- Limited by Itself: Relying solely on the pattern without considering the broader market context, fundamental factors, or other technical tools can lead to suboptimal results.
🔗 limitations
Limitations and Considerations
While the inverse head and shoulders pattern is a popular reversal indicator, it has limitations that traders must consider:
- Not Always Reliable: Just because the pattern appears does not guarantee a successful reversal. Context matters. For example, if the overall market is in a strong downtrend, an inverse head and shoulders pattern may not have the same probability of success as it would in a more neutral or bullish environment.
- Market Conditions and News Events: External factors such as unexpected news, earnings reports, or macroeconomic data releases can override technical patterns, causing the price to move unpredictably.
- Time Frame Discrepancies: Patterns on lower time frames can be more susceptible to noise, resulting in false signals. On the other hand, patterns on higher time frames may be slower to confirm, requiring patience and larger stop-losses.
- Volume Considerations: Low-volume breakouts are more prone to failure. While volume confirmation can add strength to the setup, not all markets or instruments have reliable volume data, which can make confirmation more challenging.
Understanding these limitations can help traders approach the inverse head and shoulders pattern with realistic expectations and a more disciplined approach.
🔗 FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can I ensure the pattern is valid before trading it?
A: Look for a clear structure with distinct shoulders and a head, a neckline that is respected multiple times, and a breakout on higher volume. Waiting for a retest of the neckline can also help confirm the pattern’s validity.
Q: Can the pattern occur in any market?
A: Yes, the inverse head and shoulders pattern can appear in various markets, including stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. It’s important to adjust your approach based on the characteristics of the asset you’re trading.
Q: What’s the difference between a regular and an inverse head and shoulders pattern?
A: A regular head and shoulders pattern signals a bearish reversal at the end of an uptrend, while an inverse head and shoulders pattern signals a bullish reversal after a downtrend. The shape is essentially the same but flipped upside down.
Q: How can I measure the potential price target?
A: Measure the vertical distance from the lowest point of the head to the neckline. Add this distance to the breakout point above the neckline to project the potential price target.
Q: What if the pattern fails after the breakout?
A: If the price fails to hold above the neckline and moves back below it, it’s often a sign that the pattern is invalid. In such cases, it’s crucial to have a stop-loss in place to limit losses and reevaluate the market conditions.
ফিরে যান ফিরে যান